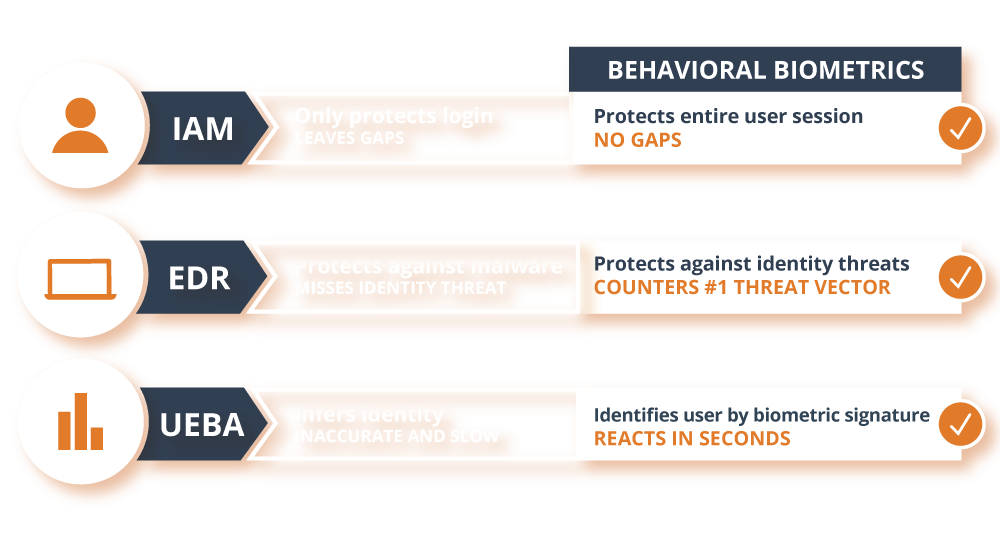
Behavioral Biometrics
Behavioral Biometrics History, Applications, and Technology
The Industry Today
“The field of behavioral biometrics is growing rapidly. Enabled by advances in computing power, behavioral biometrics is moving from the lab to the corporate or governmental office. Who’s involved and what’s the value of the industry now? Let’s take a look.

Pure Plays vs. Incorporators
Two types of companies are in the behavioral biometrics business today: we’ll call them “pure plays” and “incorporators.”
The Pure Plays
Pure plays like Plurilock offer behavioral biometrics technologies as a core product, and are focused on building and offering these technologies. Pure plays have been the driving force behind the scientific and business growth of behavioral biometrics in recent years.
Plurilock was born from this kind of focused, groundbreaking work, led in 2006 by current management team member Dr. Issa Traore and research partner Dr. Ahmed Awad E. Ahmed at the University of Victoria.7
The Incorporators
Incorporators provide or employ the behavioral biometrics technologies that pure plays develop, usually as part of a larger product or service. They choose to deploy behavioral biometrics because it enables their business or organizational purposes.
One very prominent incorporator is DARPA, the well-known U.S. government research agency responsible for the development of the Internet. DARPA now relies on behavioral biometrics as a key dimension of its organizational security model (see below).
THE DARPA ACTIVE AUTHENTICATION PROGRAM
The U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) was a major force behind the initial growth of behavioral biometrics, which paved the way for companies like Plurilock to perfect the technology.
DARPA’s pioneering Active Authentication (AA) Program, launched in 2012, sought to enhance security across the US military by complementing traditional authentication methods like passwords with behavioral biometrics approaches.
The two phases of DARPA’s AA roll-out led to findings and refinements that have been critical to the widespread—and still growing—adoption of behavioral biometrics technologies.
AA PHASE I: User Analysis

In this phase, DARPA conducted a far-reaching analysis of behavioral traits in computation. These included keystroke patterns and mouse movements.
AA PHASE II: Technology, development, and implementation.

In this phase, DARPA used its Phase I findings to develop a new tools capable of validating users' identities based on computational-behavioral traits.
Machine learning and the GROWTH of Behavioral Biometrics
Big data has been a growing obsession in science, government, and business for over a decade now. Global networks, billions of mobile devices, and a new “internet of things” have produced unprecedented amounts of data that humans alone could never hope to analyze or understand. Artificial intelligence, which enables computers to analyze and make use of this data, has exploded as a result.
The subfield of artificial intelligence research known as “machine learning” has been a key enabler in the continued growth of behavioral biometrics.
Machines that learn are able to astutely refine or enhance their own capabilities as they perform key tasks or encounter data related to these tasks—just what’s needed for behavioral biometrics technologies to “learn about” user behavior and gradually evolve with it over time.
The advances in machine learning that have occurred over the last decade have thus resulted in a seismic shift in behavioral biometrics—taking it from a largely research-oriented field to a portfolio of market-ready technologies ideal for use in industry.
Filling the Gap: Customer
Experience Meets CyberSecurity
Today’s customers expect smooth experiences that are free of complications or stumbling blocks. Brands that do this well succeed, those who fail may lose business. Along with user experience, cybersecurity is a hot topic— awareness is at an all-time high. Password-based and two-factor authentication methods are currently industry standard, and while these reassure some customers, they interrupt the sales process for many others who turn away in frustration.
In other words, the current practices in cybersecurity and user experience design are at odds with one another. Behavioral biometrics is increasingly being used to fill this gap—by adding a secure, data-driven authentication layer that adds no friction to users’ experiences.

Behavioral Biometrics and the Employee Experience
Think about employees as internal customers. They experience the same frustrations balancing security and ease of use but, while a customer may only have infrequent interactions with the brand, employees are interacting with the systems daily. Being able to protect their endpoints without added “hoops to jump through” keeps employees happy and reduces helpdesk burden, improving efficiency and security at the same time. Behavioral biometrics can add this additional, invisible layer of security, letting employees get on with their work.
7. Traore, D., and Ahmed, A. 2012. Continuous Authentication Using Biometrics: Data, Models, and Metrics. University of Victoria.
Machine learning and the GROWTH of Behavioral Biometrics

Customer-Focused Web Application Protection
Exclusively Static Authentication

Identity Assurance
for the workplace

PLURILOCK
Benefits
- Invisible and frictionless to users
- Continuous protection
- Zero impact on system performance
- Machine Speed